Documentation & FAQ v
RARe-SOURCE™ - Integrated Bioinformatics Resource for Rare Diseases
NCATS has partnered with the Advanced Biomedical Computational Science group at NCI-Frederick to collect & integrate multiple data sources to develop an integrated bioinformatics resource to address the challenges in rare disease research.
Goals
- Identify bioinformatics databases
- Establish an accessible and searchable resource
- Discover commonalities among inherited disorders
- Advance translational research to improve diagnosis and treatment
Challenges

Data, Data, Everywhere & Nowhere
- Accessibility
- Integration
- Analysis
- Interpretation
- Dissemination
Objectives

- Develop an innovative application and searchable interface for data mining
- Establish tools for analyzing OMICS data from disease cohorts and public/private data sources
- Connect human genotype-phenotype- molecular associations with disease model systems data
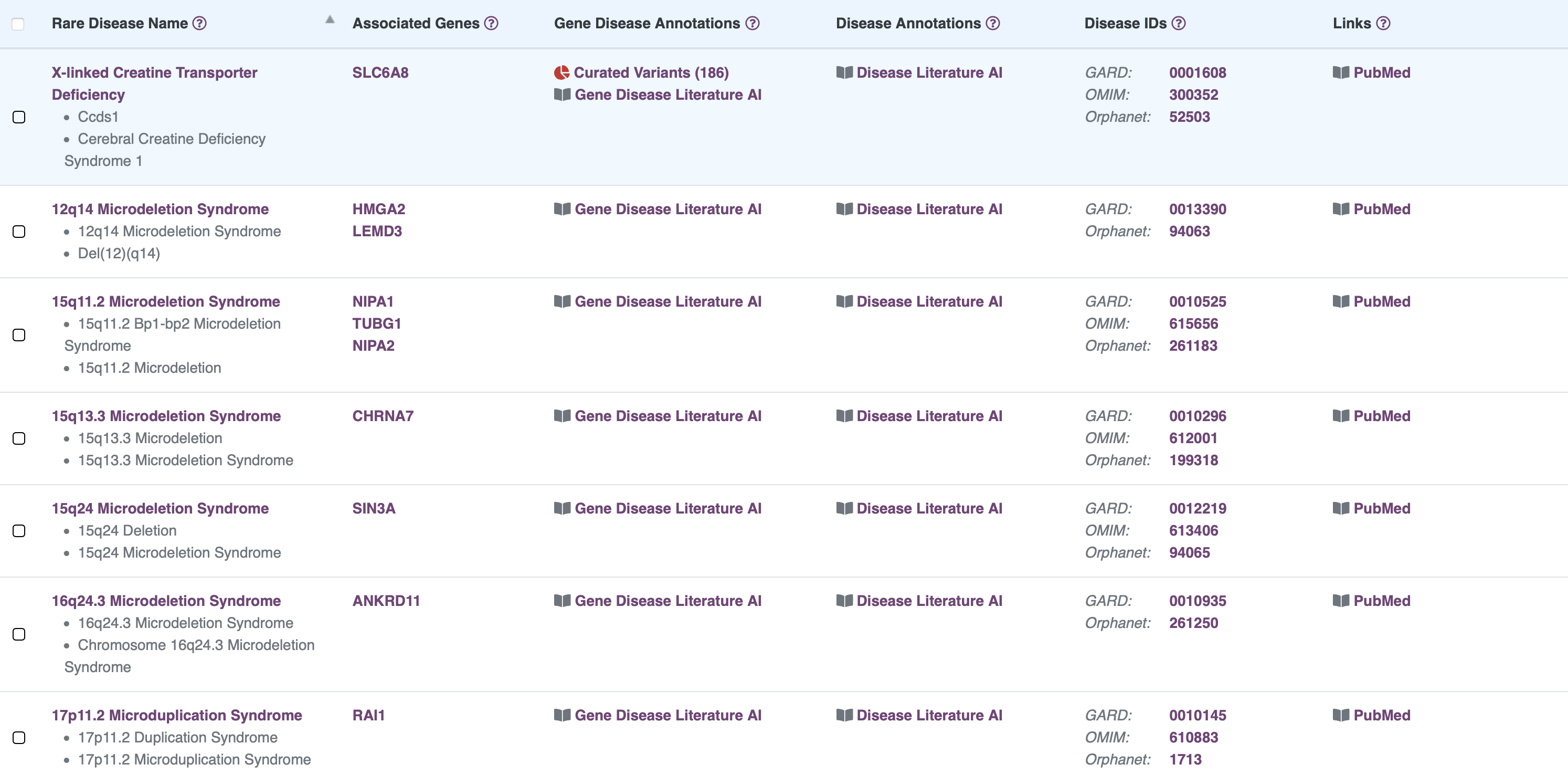
Browse Rare Disease Information
RARe-SOURCE™ integrates multiple data sources to provide researchers and visitors the ability to view detailed rare disease information presented in an efficient and easy to navigate layout.
Features:
- Information on rare diseases with genetic etiology
- Disease synonym information
- Publications related to selected rare disease
- Disease IDs with links to other rare disease information sources
- Links to related gene details in RARe-SOURCE™
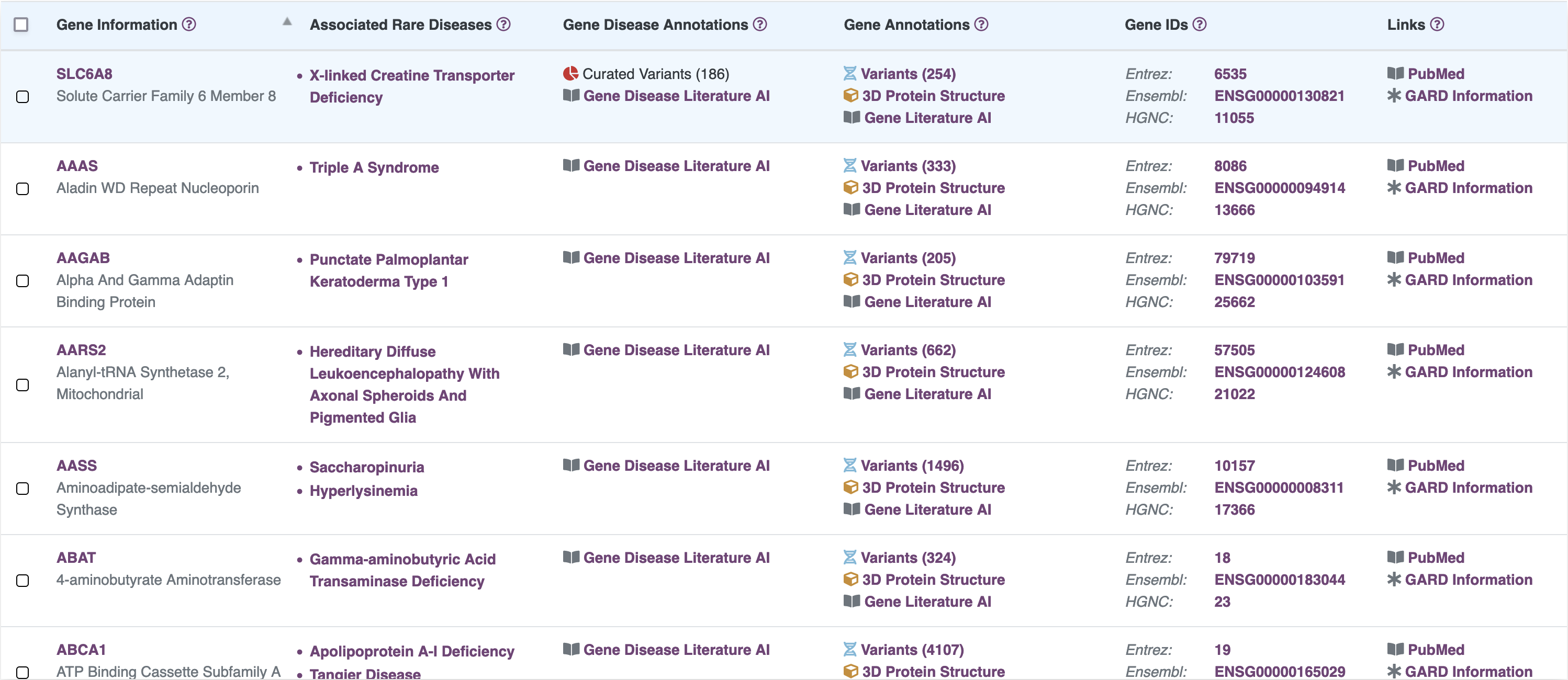
Browse Gene Information
RARe-SOURCE™ integrates multiple data sources to provide researchers and visitors the ability to view detailed gene information presented in an efficient and easy to navigate layout.
Features:
- Information on genes associates with rare diseases
- Details on genomic variants identified in the gene
- Manually curated variant annotations for SLC6A8
- 2-dimensional protein structure provided by ProtVista
- 3-dimensional protein structure provided by MolArt
- Integrated protein feature and variant details
- Publications related to selected gene
- Links to related disease details in RARe-SOURCE™
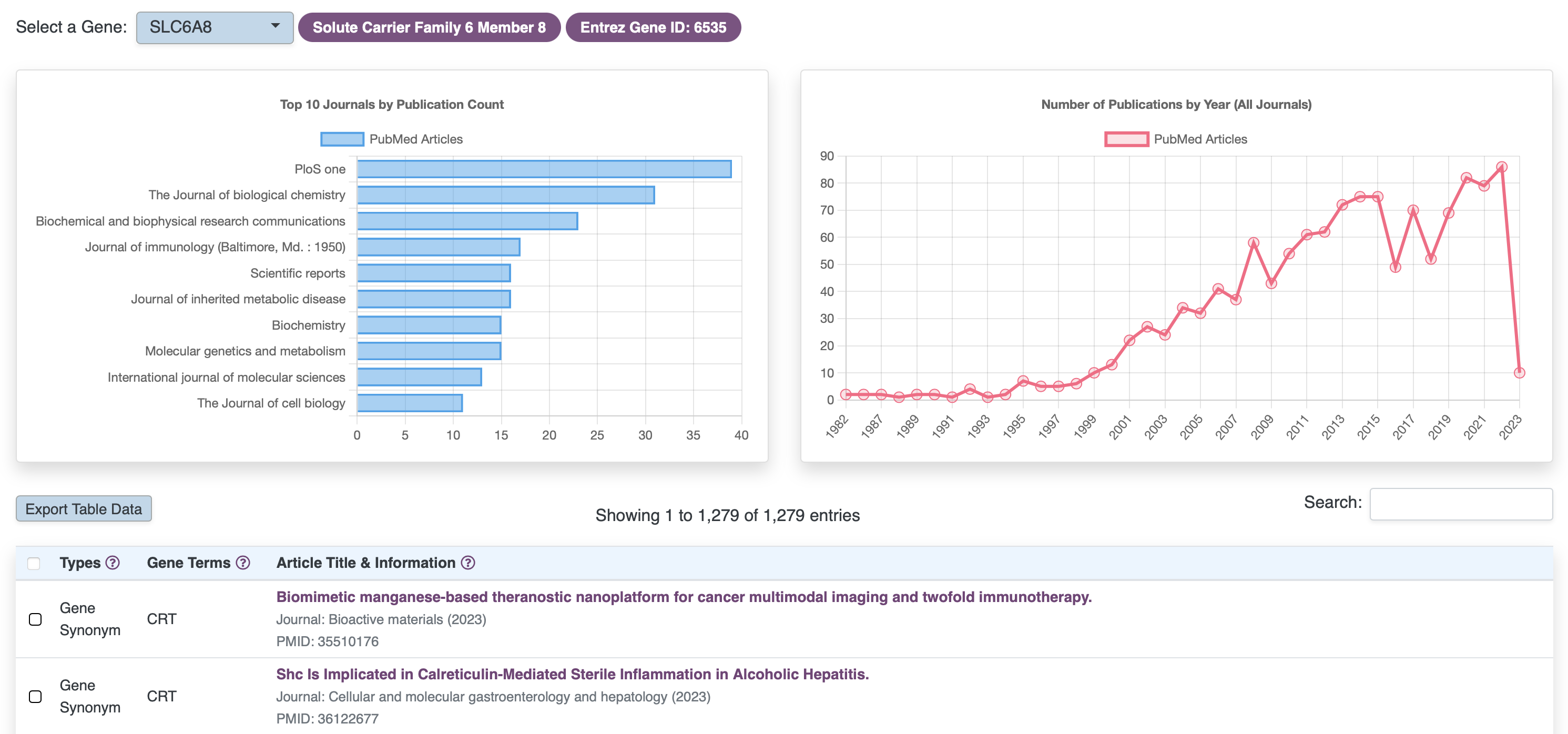
Browse Literature
RARe-SOURCE™ implemented Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms for identifying disease and gene mentions in titles or abstracts of published literature.
Features:
- Information on published literature for rare diseases and associated genes
- Integration of primary rare disease names and aliases
- Integration of gene symbols, aliases, descriptions, keywords and other naming conventions
- Integrated searches with rare diseases and their associated genes, so literature where both rare diseases and their associated genes have been mentioned can be easily referenced
- Show trends on the publications over the years
- Display top journals where the literature has been published
- Link outs to PubMed, to access the details on any article
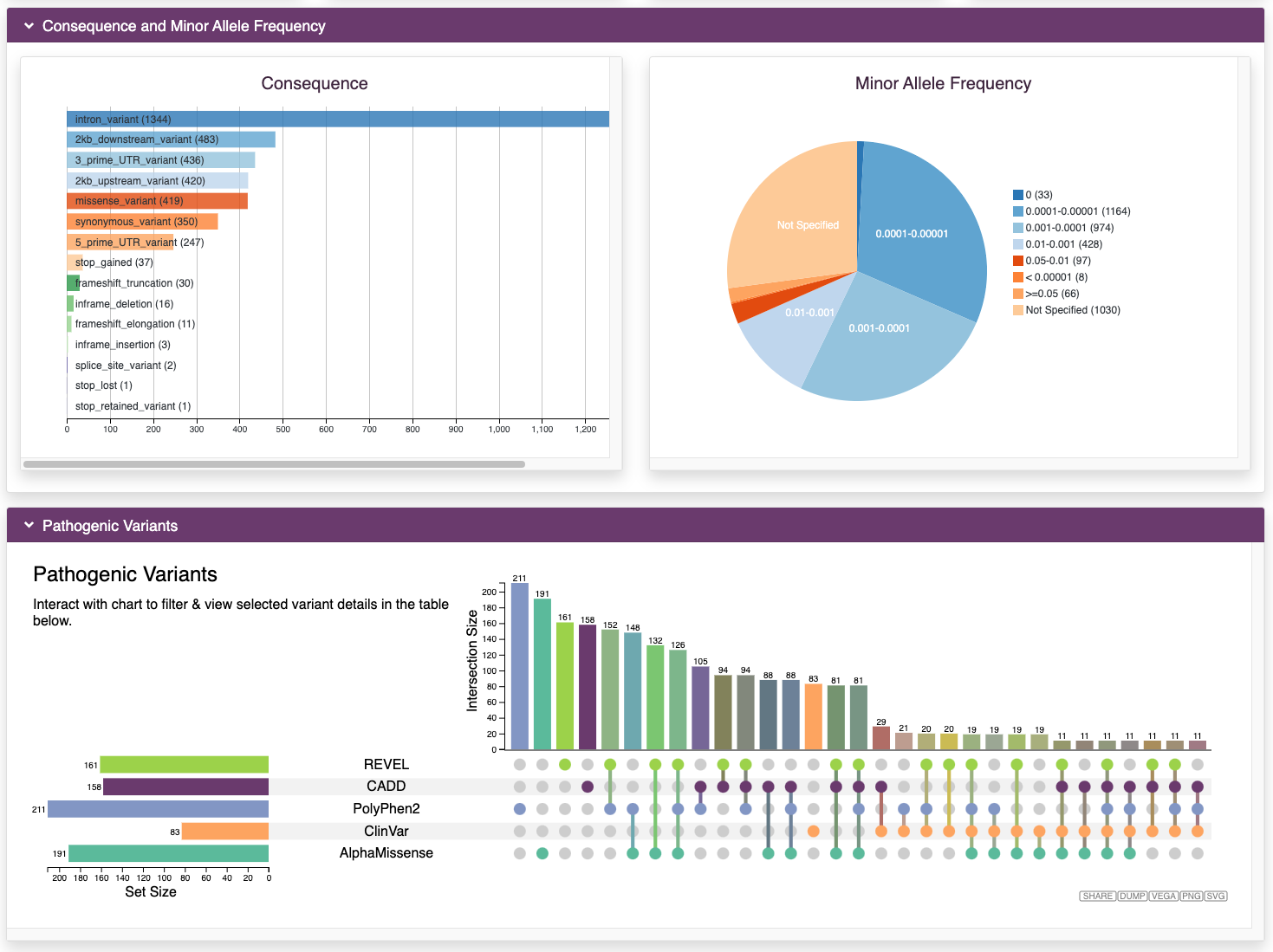
Browse Variants
RARe-SOURCE™ gathered millions of variants in genes associated with rare diseases. The variants were downloaded from many public data sources and annotated using OpenCRAVAT.
Features:
- Annotations for variants in genes associated with rare diseases
- Minor allele frequency (MAF) from many population studies
- Maximum MAFs calculated and made available wherever possible
- Visualizations for the number and type of different variants in each gene
- Pathogenic variants from ClinVar and from multiple impact prediction algorithms
- Integration of predictions from AlphaMissense
- Interactive visualizations to filter variants based on MAF scores
Browse Curated Variants
Information on pathogenic variants is vital for disease diagnosis as well as research on therapeutic approaches. Despite being published in the literature, pathogenicity data on patient variants may not be accessible through a public resource. Our researchers have read peer reviewed manuscripts indexed in MEDLINE and PubMed to create a curated list of published variants for SLC6A8.
Features:
- Curated details from 216 published peer reviewed manuscripts including reports of individual X-Linked Creatine Deficiency patients, modeling of protein folding topology and the impact of genetic variants on signaling pathways, and reviews, dating from 1975 to 2019
- Highly annotated dataset of variants with clinical context and functional details
- All variants harmonized to standard notations
- Customize columns to include in the tabular view and download
- Interactive visualizations and filtering options
- Pathogenic variants displayed along the 2D protein location along with bars with lengths corresponding to the measured creatine uptake where available
Q: What Rare Diseases does RARe-SOURCE™ provide information
on?
A: A: RARe-SOURCE™ provides details on rare diseases with genetic etiology and
their
associated genes. Information on the diseases and their associated genes is obtained
from genetic and rare diseases (GARD) database and in the current version does not
include all rare diseases with genetic etiology. For the literature AI and variant
annotations, additional genes and known associations were obtained from OrphaNet and
Ehrhart et. al., Sci Data, 2021
Q: How reliable are the literature AI details?
A: RARe-SOURCE™ implements artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to identify
rare
disease and associated gene mentions in the titles and/or abstracts of published
literature. The algorithms do not yet identify all possible mentions and might miss out
some valid results. We are actively working on validating and improving the algorithms
and the search results are expected to get better over time.
The results obtained from
the AI algorithms are combined with the information on different disease and gene
aliases to obtain articles where the disease or gene terms might be mentioned using a
different naming convention. Although, this allows RARe-SOURCE™ to find more
articles
related to the rare disease or gene of interest, it also has an increased probability of
finding results that might not be relevant. In the current version, RARe-SOURCE™
leans
towards finding more articles than losing any that might be relevant.
RARe-SOURCE™
automatically prioritizes results within each publication year, so that the most
relevant results are floated to the top. The titles for each of the results are also
prominently displayed and the articles are linked to PubMed, so any of the results can
be quickly reviewed and verified.
Q: Why are there no literature AI results for some genes or rare
diseases?
A: We strive to comprehensively cover all concepts from the literature. However, text
variations in disease names can sometimes pose challenges in accurate identification.
Our approach utilizes advanced name recognition and relies on specific data sources,
including the Genetic and Rare Diseases (GARD) resource, for identifying rare diseases.
Despite these efforts, it is possible that we may not be able to identify all the
variations in disease names comprehensively. We endeavor to address this limitation by
dedicating additional effort to respond to requests for the inclusion of specific
diseases not identified by our methods. We have integrated additional diseases and gene
associations from OrphaNet and Ehrhart et. al., Sci Data, 2021 but realize they do not
cover all rare diseases of interest. Feel free to
contact us if you do not see your
disease or gene in our resource, and we will make every effort to include it manually.
Our goal is to enhance accuracy and inclusivity in biomedical information.
Q: How are the variant details obtained?
A: RARe-SOURCE™ implements a combination of variant data integration and manual
curation
for providing genomic variant details. Variants for all genes in RARe-SOURCE™ are
obtained by integrating public variant databases and annotating them using OpenCravat.
Manual curation of published literature is performed for specific diseases and
associated genes. Manual curation is completed, and results are available for SLC6A8
(X-linked creatine transporter deficiency). We are currently in the process of manually
curating ASAH1 (Farber disease) variants.
Q: What is MAF for a variant?
A: "MAF" stands for Minor Allele Frequency. It represents the frequency at which the
less common allele, in this case a variant, occurs in each population. It is a measure
of how often it appears among all the individuals sequenced as part of a study. MAF is
used for understanding genetic diversity and for identifying alleles that may be
associated with specific traits or diseases. A higher MAF (generally at > 5%) indicates
that the variant is relatively common in the population, whereas a lower MAF suggests
that the variant is rarer. MAF is often used in genetic research to filter variants,
prioritize findings, and assess the potential significance of variants in disease
association and risk assessment.
Q: How is the maximum Minor Allele Frequency (MAF) determined?
A: The highest allele frequency is determined by selecting the value of the greatest
minor allele frequency across all population studies included in our database. These
studies encompass gnomAD2, gnomAD3, thousand genomes, complete
genomes 69, NCI60, HGDP
European, GME, ESP6500, ExACNONTCGA,
UK10K Cohort,
and Alfa. The population/study
corresponding to the maximum MAF is reported in the Max MAF Source.
Q: How is pathogenicity determined for ‘Annotated Variants’ in the 2D/3D protein
visualizations?
A: Variants annotated by RARe-SOURCE™ are displayed as ‘Annotated variants’ in the 2D
and 3D protein visualizations. The clinical significance value from ClinVar is used for
the pathogenicity impact values. Variants not in ClinVar are annotated as ‘No ClinVar
annotation’.
Q: Do I need to request an account or special access in order to view rare
disease information?
A: At this time, RARe-SOURCE™ allows users to access rare disease and gene
information
without logging in. In the future, RARe-SOURCE™ may require certain users to be
authenticated to access sensitive data, save dashboard information or share research
with other users of the resource.
A: RARe-SOURCE™ focuses on genotype-phenotype correlations for rare diseases and integrating related data from a variety of databases with the goal of:
- Providing easy access to published literature on rare diseases without having to know and/or search for all associated disease and gene names and aliases.
- Making variant annotations and impact assessments available for genes associated with rare diseases.
- Mapping variants on the three-dimensional structure to assist researchers in investigating structure function relationships and the impact of the variant on the protein’s ability to interact with signaling partners.
A: RARe-SOURCE™ allows for data export in multiple formats:
- All Tabular data can be copied to system clipboard or exported in CSV or Microsoft Excel compatible formats.
- 2-D protein structure visualization data can be exported by ProtVista in JSON format.
- 3-D protein structure visualizations can be exported or downloaded in PNG graphical image format.
Q: Can I upload my own Gene or Rare
Disease information to RARe-SOURCE™?
A: Currently, RARe-SOURCE™ integrates data from multiple internal and external
sources
that are frequently updated. This ensures that we present the most up-to-date
information on Rare Diseases and Gene Variants. Future plans include features which will
allow users to input their own variant or rare disease information.
RARe-SOURCE™ Release Notes & Information
Version 1.2.0 - 2024-07-29
New Features and Enhancements
1. Browse Gene Variants
- Layout Overhaul: The gene variants page has undergone a complete redesign for improved user experience and aesthetics.
- Summary Card Filters: Additional filtering functionality has been added to the summary cards at the top of the page, allowing for more refined searches.
- Direct Gene Browsing: A new dropdown menu at the top of the gene variants page allows users to browse different genes directly, streamlining the navigation process.
- Direct Links to 3D Protein Structures: Users can now access 3D protein structures directly from the Variants and Manually Curated Variants tab via newly added hyperlinks.
2. Enhanced Literature AI Functionality
- Advanced Filtering/Search: New search panes have been added above tables, providing enhanced filtering and search capabilities within the Literature AI section.
- Improved User Instructions: Enhanced instructions and directions are now available throughout the Literature AI section, making it easier for users to navigate and utilize the features.
3. Browse Genes and Diseases
- Literature AI counts: The Browse Genes and Diseases tables now display available Literature AI counts next to each hyperlink, giving users immediate insight into the number of related literature entries.
General Improvements
- Site-Wide Translation: Google Translation is now available site-wide, accessible from the footer on every page. Users can translate the content into any international language, enhancing accessibility for non-English speakers.
Bug Fixes
- Resolved Minor Bugs: Various minor bugs reported in the previous version have been fixed, ensuring a more stable and reliable application.
Version 1.1.1 - 2024-02-28
General Improvements
- Performance Optimizations: Visualization optimizations for faster load times and smoother user experience on interactive charts.
Bug Fixes
- Resolved Minor Bugs: Addressed minor bugs from the previous version for a more stable and reliable application.
Version 1.1.0 - 2024-02-23
New Features and Enhancements
1. Browse Gene Variants
- Interactive Visualizations: Allows selection and filtering of variants by type, genic location, minor allele frequency, or pathogenicity predictions.
- Manually Curated Variants: Displays clinical and functional details of variants from literature, currently available for SLC6A8 (X-linked creatine transporter deficiency).
2. Browse Literature AI
- AI-Enhanced Literature Search: Utilizes AI algorithms to search literature for mentions of rare diseases and associated genes.
- Integrated Results: Displays results integrated with disease aliases and gene naming conventions.
- Publication Trends: Charts show publication trends over the years and across journals.
General Improvements
- User Interface Enhancements: Minor UI adjustments across various sections for improved usability and visual appeal.
- Performance Optimizations: Backend optimizations for faster load times and smoother user experience.
Bug Fixes
- Resolved Minor Bugs: Fixed various minor bugs from the previous version for a more stable and reliable application.
Version 1.0.0 - 2023-02-28
New Features and Enhancements
1. Browse Genes
- Comprehensive Gene Table: Displays a list of all genes associated with rare diseases within RARe-SOURCE™.
- Gene Details: Clicking on a gene name shows its genomic location, disease associations, and recent PubMed publications.
- Rare Disease Links: Clicking on an associated rare disease leads to the ‘Rare Disease Information’ page.
2. Browse Diseases
- Detailed Disease Table: Lists all rare diseases within RARe-SOURCE™ along with their gene associations.
- Disease Aliases and Publications: Clicking on a disease name displays its aliases and recent PubMed publications.
- Gene Links: Clicking on an associated gene leads to the ‘Gene Information’ page.
3. Browse Gene Variants
- Variant Annotations: Provides a tabular listing of variants from multiple databases with annotations.
- 3D Protein Structure Visualization: Offers an integrated 2D-3D view of protein features from UniProt on the protein structure.
General Improvements
- User Interface Enhancements: Minor UI adjustments across various sections for improved usability and visual appeal.
- Performance Optimizations: Backend optimizations for faster load times and smoother user experience.

