Our Mission
Our mission is to accelerate rare disease research and therapeutic discovery by integrating diverse, siloed data into a unified, user-friendly platform. By harmonizing information on rare diseases, their phenotypes, associated genes, genetic variants, and more, we help researchers and community partners uncover meaningful molecular connections, generate new hypotheses, and advance the development of treatments for rare disorders.
Developed by NCATS’ Therapeutic Development Branch in collaboration with the Frederick National Laboratory’s Advanced Biomedical Computational Science Group, RARe-SOURCE®, an integrated bioinformatics resource for rare diseases, provides an innovative, data-driven foundation to support scientific insight and translational impact.
- Data is fragmented and stored across different systems, platforms, and organizations
- Domain-specific research limits discovery of shared commonalities
- Small sample sizes in rare diseases pose challenges for meaningful analysis
- Scientific, technical and translational gaps in transforming data to actionable insights
Integrate and enrich biomedical data to uncover commonalities and disseminate actionable knowledge that advances translational science and therapeutic discovery for rare diseases.
- Integrate heterogenous datasets including rare disease patient data to strategically identify commonalities
- Leverage large language models to mine rich contextual knowledge from complex biomedical data
- Customize workflows integrating insights from manual curation, artificial intelligence models, and data annotations
- Build a platform where information can be shared through interactive tables and visualizations
Explore Our Tools
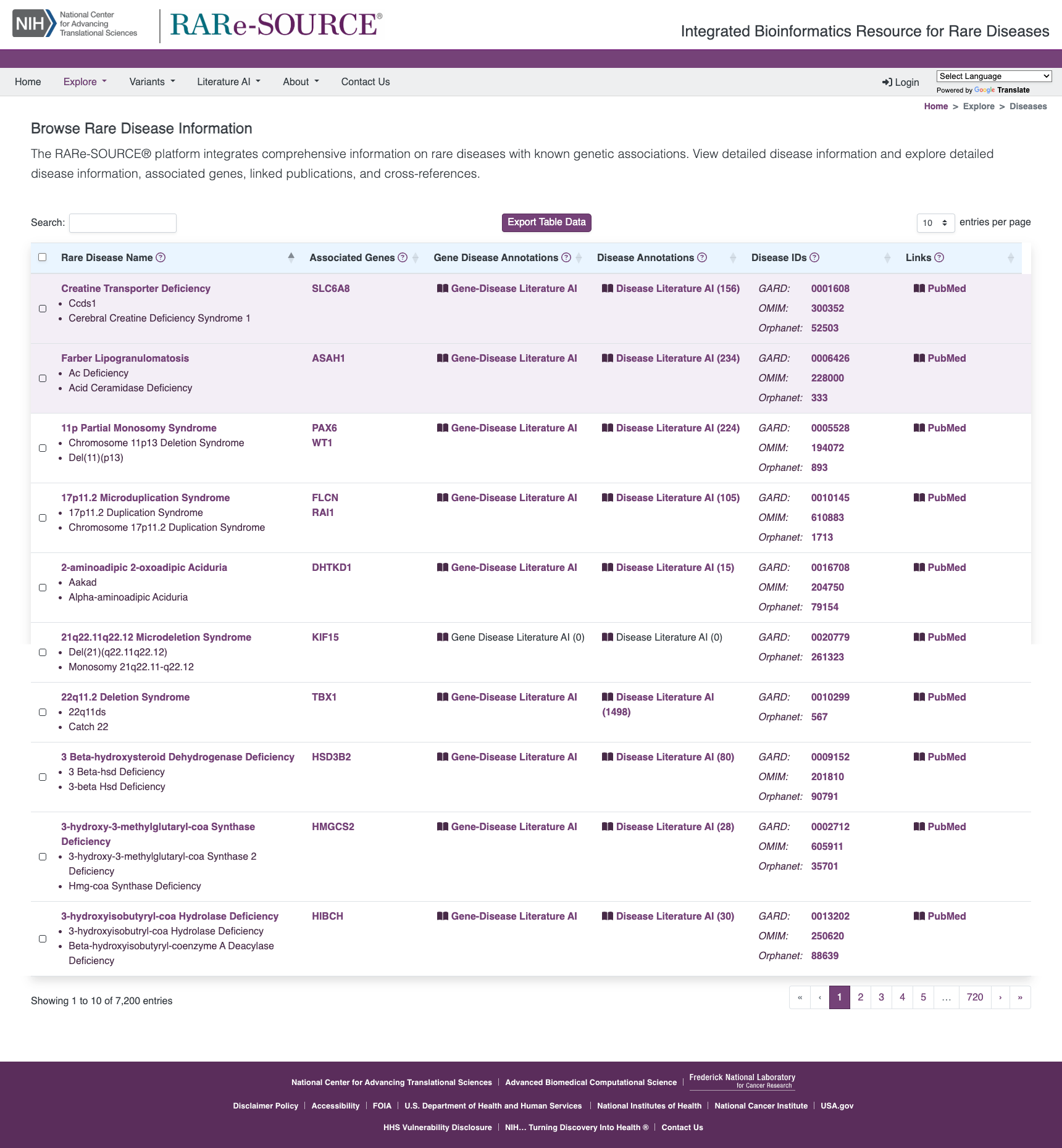
Browse Rare Disease Information
The RARe-SOURCE® platform integrates multiple data sources to provide researchers and visitors the ability to view detailed rare disease information presented in an efficient and easy to navigate layout.
Features:
- Information on rare diseases with genetic etiology
- Disease synonym information
- Publications related to selected rare disease
- Disease IDs with links to other rare disease information sources
- Links to related gene details in The RARe-SOURCE® platform
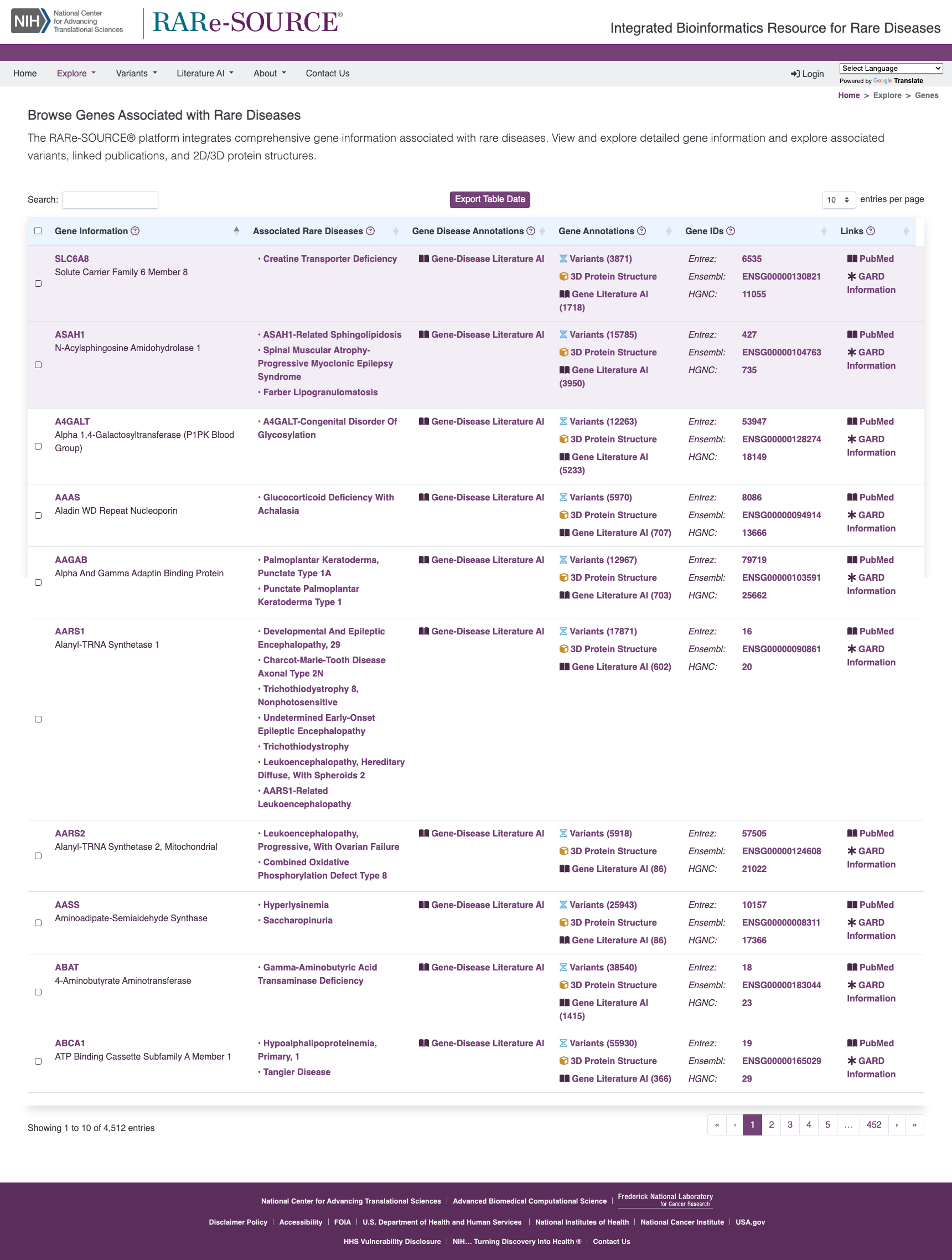
Browse Gene Information
The RARe-SOURCE® platform integrates multiple data sources to provide researchers and visitors the ability to view detailed gene information presented in an efficient and easy to navigate layout.
Features:
- Information on genes associated with rare diseases
- Details on genomic variants identified in the gene
- Manually curated variant annotations for SLC6A8
- 2-dimensional protein structure provided by ProtVista
- 3-dimensional protein structure provided by MolArt
- Integrated protein feature and variant details
- Publications related to selected gene
- Links to related disease details in RARe-SOURCE®
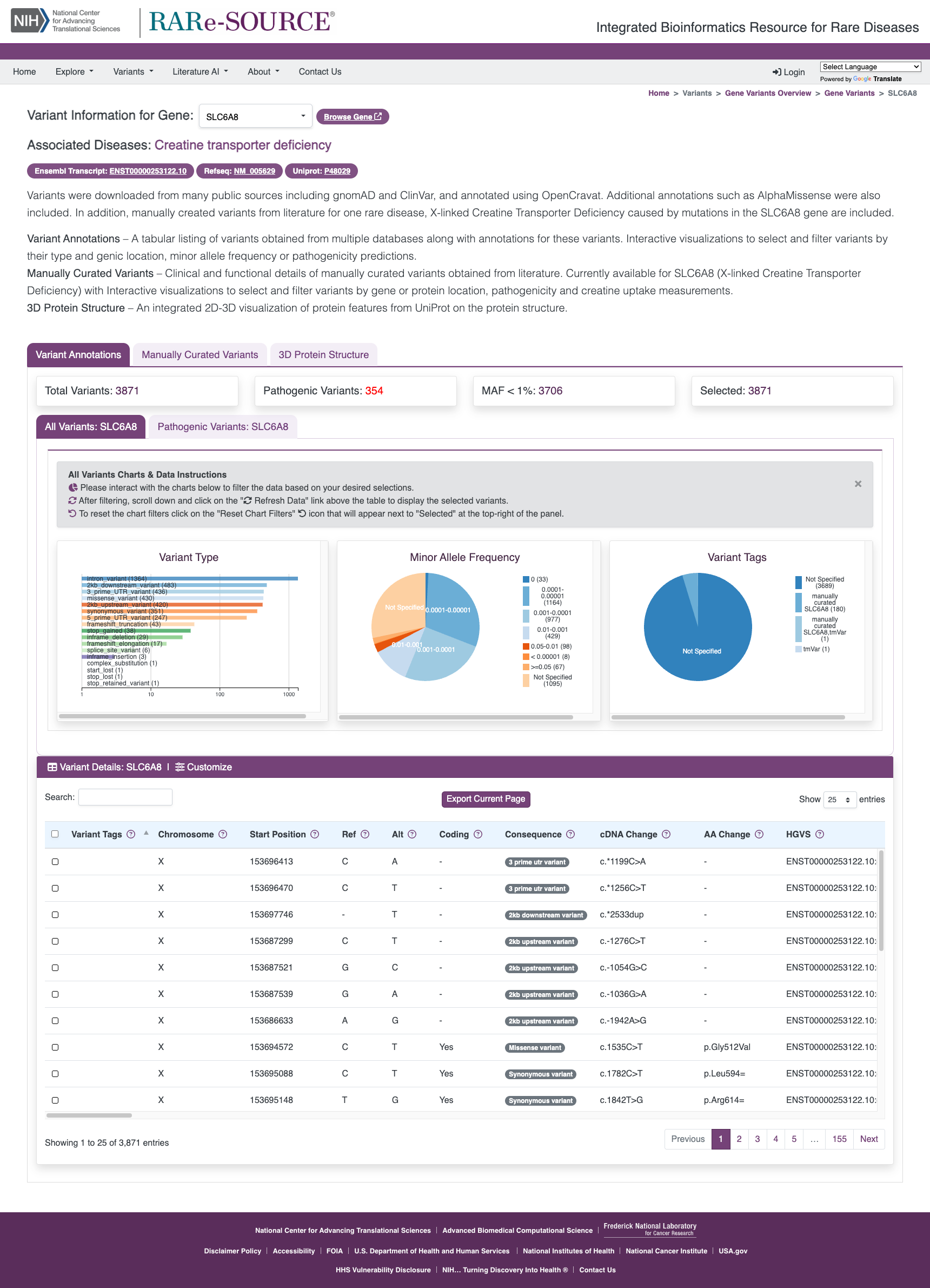
Gene Variants
The RARe-SOURCE® platform gathered millions of variants in genes associated with rare diseases. The variants were downloaded from many public data sources and annotated using OpenCRAVAT.
Features:
- Annotations for variants in genes associated with rare diseases
- Minor allele frequency (MAF) from many population studies
- Maximum MAFs calculated and made available wherever possible
- Visualizations for the number and type of different variants in each gene
- Pathogenic variants from ClinVar and from multiple impact prediction algorithms
- Integration of predictions from AlphaMissense
- Interactive visualizations to filter variants based on MAF scores
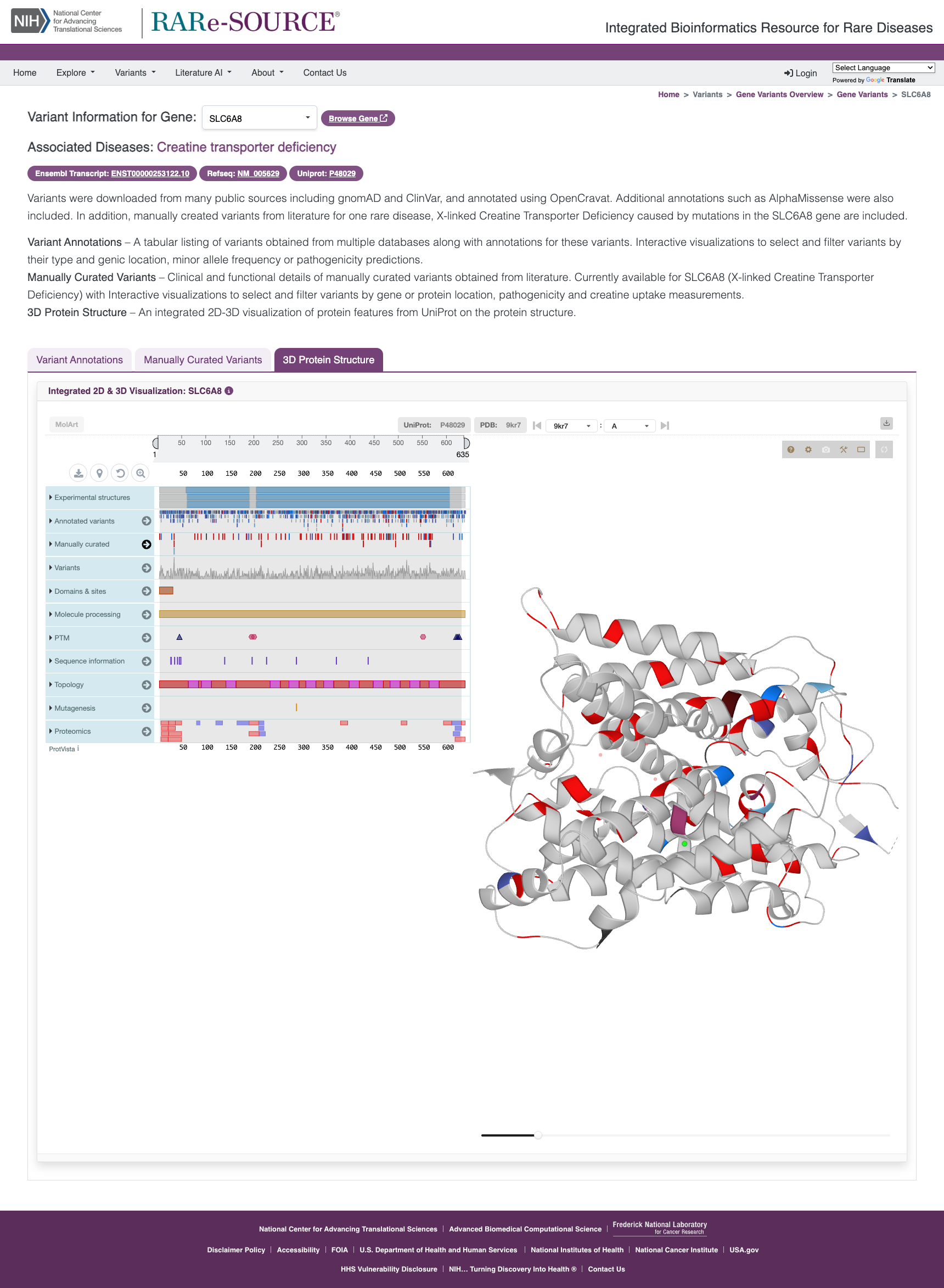
2D/3D Protein Visualization
Analyze 2D/3D protein structure to find functional impact of public, annotated, and curated variants.
Features
- Visualization of protein structure
- Annotation of protein sequence
- Adjustable protein sequence window
- Highlighting capabilities of sequence, feature, and structure
- Color overlay of sequence features
- Transparency control for cartoon view and surface view
- Analyze consequences and pathogenicity
- Explore annotation sources and cross references
- Export of the data, structure, and annotations
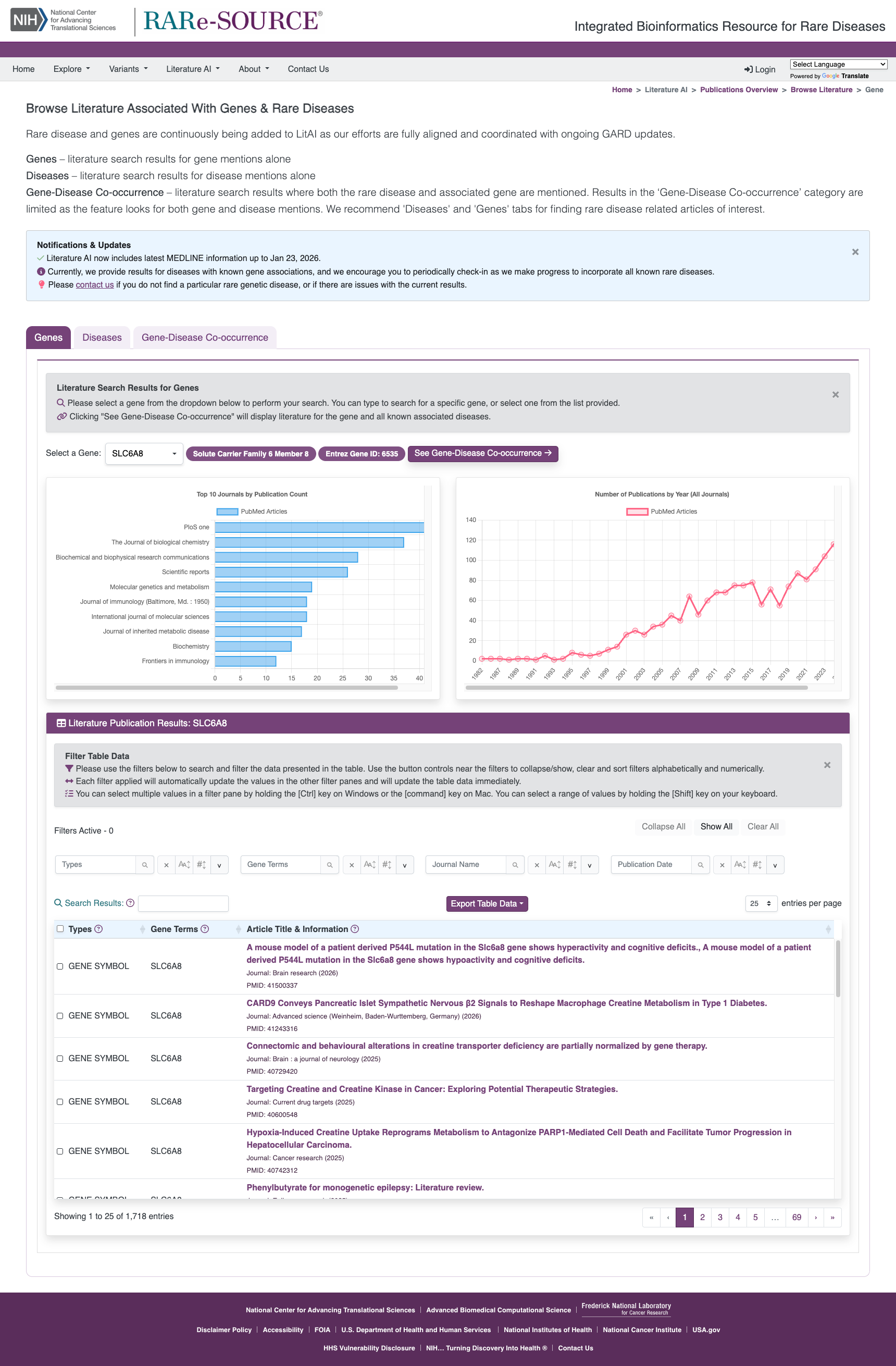
Literature AI
The RARe-SOURCE® platform implemented Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms for identifying disease and gene mentions in titles or abstracts of published literature.
Features:
- Information on published literature for rare diseases and associated genes
- Integration of primary rare disease names and aliases
- Integration of gene symbols, aliases, descriptions, keywords and other naming conventions
- Integrated searches with rare diseases and their associated genes for co-occurrence
- Show trends on publications over the years
- Display top journals where the literature has been published
- Link outs to PubMed to access article details
Project Collaborators

The NCATS Therapeutic Development Branch (TDB) aims to advance the field of drug development by encouraging scientific and technological innovations to improve success rates in the crucial preclinical stages of drug development. To support translational research, The Therapeutics for Rare and Neglected Diseases (TRND) program within TDB initiated the RARe-SOURCE® platform, an open access application for researchers, clinicians, and patients with a searchable interface for data mining and querying bioinformatics resources. The objectives are to unlock novel insights into disease commonalities, attempt to accurately determine prevalence, and identify potential new therapeutic targets and therapies.
Learn More
The Advanced Biomedical and Computational Science (ABCS) group at the Frederick National Lab serves as a hub of translational scientists with expertise in machine learning applied to the interpretation of 2D and 3D biomedical images, clinical and genomics integration, computational chemistry, protein modeling, bioinformatic analysis of omics data, and other applications of computational and data science. ABCS develops state-of-the-art technologies in large-scale data modeling, analysis, and integration and supports the scientific research at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and National Institutes of Health (NIH) by helping translate scientific questions to technical solutions for cancer and biomedical research.
Learn More
NICHD’s Section on Molecular Dysmorphology headed by Dr. Forbes D. Porter investigates molecular, biochemical, cellular, and developmental processes that underlie genetic syndromes with the goal to combine both basic science and clinical expertise to develop and test novel therapeutic interventions. In collaboration with NCATS, a natural history study (NHS) was initiated to study children with creatine transport deficiency (CTD) at the NIH Clinical Center. This study is part of a multicenter CTD NHS effort with the goal to obtain detailed disease data, establish a biorepository, identify biomarkers and potential clinical outcome measures in preparation for therapeutic clinical trials. CTD has provided an initial test case for the literature extraction of genetic variants and pathogenicity to better understand their impact on disease.
Learn More
NINDS’s Neuromuscular and Neurogenetic Disorders of Childhood Section (NNDCS) led by Dr. Carsten G. Bönnemann focuses on investigating molecular mechanisms underlying early onset neuromuscular disorders of childhood (including congenital muscular dystrophies, myopathies, and myasthenic syndromes, as well as early onset motor or sensory neuron disease) with the goal to understand the genetic and cellular mechanisms in these conditions. The overall objective is to develop molecular-based treatments by pursuing preclinical and clinical translational models and methods to lead to clinical trials. NINDS is collaborating with RARe-SOURCE® to advance knowledge related to the genetic basis and underlying disease mechanisms to classify the congenital muscular dystrophies and link them to precise molecular treatment approaches.
Learn MorePosters, Presentations, and Awards
Presentation listings to be added.
Lyons, E.L., Watson, D., Alodadi, M.S. et al. Rare disease variant curation from literature: assessing gaps with creatine transport deficiency in focus. BMC Genomics 24, 460 (2023). Read Publication
NIH & NCATS Director’s Awards 2023
Conception and development of RARe-SOURCE®, an innovative bioinformatics data platform to facilitate therapeutic discovery and advance translational science more quickly for rare diseases.
Data Sources
Our goal is to integrate a variety of data sources to uncover connections and generate hypotheses to advance the development of treatments for rare disorders. To achieve this our researchers have pulled together data from various sources. We are continually researching and updating relevant data sources under the appropriate FAQ
Cite Us
If you use RARe-SOURCE®, an integrated bioinformatics resource for rare diseases, in publications, presentations, or reports, please cite the website
Suggested Resource Citation (NLM/Internet format)
RARe-SOURCE® [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), National Institutes of Health (NIH); [cited YYYY Mon DD]. Available from: https://raresource.nih.gov/
Good Citation Practice
- Include an access date when citing online NIH resources.
- Use the citation style required by your target journal (NLM, AMA, APA, or Vancouver).
- If specific pages, figures, or datasets are used, cite the exact page URL when possible. Reference guidance: NLM Citing Medicine, NIH database citation example (NCI BRD), and NIH webpage citation practices (NIMH).
If SLC6A8 and/or Creatine Transporter Deficiency manually curated variants are used, also cite the associated publication:
Lyons EL, Watson D, Alodadi MS, et al. Rare disease variant curation from literature: assessing gaps with creatine transport deficiency in focus. BMC Genomics. 2023;24(1):460. doi:10.1186/s12864-023-09561-5.
Help
Not sure what to do? Check out our tools, look for the tooltip icons throughout the site for guidance , or get in touch below for more help.
For feedback and comments, please contact us here .
